Characterization of the Lipid Structure and Fluidity of Lipid Membranes on Epitaxial Graphene and Their Correlation to Graphene Features
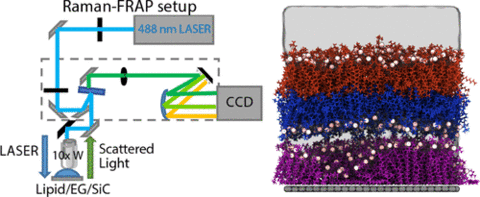
Graphene has been recognized as an enhanced platform for biosensors because of its high electron mobility. To integrate active membrane proteins into graphene-based materials for such applications, graphene’s surface must be functionalized with lipids to mimic the biological environment of these proteins. Several studies have examined supported lipids on various types of graphene and obtained conflicting results for the lipid structure. Here, we present a correlative characterization technique based on fluorescence measurements in a Raman spectroscopy setup to study the lipid structure and dynamics on epitaxial graphene. Compared to other graphene variations, epitaxial graphene is grown on a substrate more conducive to production of electronics and offers unique topographic features. On the basis of experimental and computational results, we propose that a lipid sesquilayer (1.5 bilayer) forms on epitaxial graphene and demonstrate that the distinct surface features of epitaxial graphene affect the structure and diffusion of supported lipids.